General Information on Chinese Visa Application
All foreign visitors to China need a visa. Applicants are advised to apply their Chinese visas from the Embassy or Consulate-General of Peoples’ Republic of China which holds consular jurisdiction over the state where they reside or work permanently. Visa category, validity, number of entries and duration of each stay are issued at the discretion of the consular officers whose decisions are based strictly on relevant laws and regulations of PRC, and also on the identity and purpose of trip of applicant.

We have multiple-entry China visa solutions for various nationalities. This visa allows you to enter China as many time as you want.
Basic Requirements for China Visa Application
-
Valid passport (at least six months before expiration) with blank visa pages;
-
Completed Chinese visa application form, one colored passport photo taken in the last six months;
-
Additional documents required depending on the applied visa type.
Chinese Visa Types and Requirements
There are several types of visas available. Applicants should choose one depending on their needs and purposes of travel.
1. Business/Visit Visa (F visa):
F Visa is issued to foreigners who are invited to China for a visit, an investigation, to do business, short-term advanced studies or internship for a period of no more than six months.
This visa is reliant upon a Visa Notification Form issued by the relevant Chinese authorized agency. Usually the Chinese inviting company will get this Visa Notification Form for foreign visitors. Then the foreigners could apply to the Chinese Embassy/ Consulate-General for F visa, along with other supporting documents such as a copy of return flight ticket booking.
The Visa Notification Form will indicate entry times and visa validity of the F visa the foreign applicant can apply.
2. Tourist Visa (L visa):
L Visa is issued to foreigners who come to China for sightseeing or visiting family members or friends or for other personal affairs.
Applicants can apply for single entry, double entry, or multiple entry visas. L visa is fairly easy to obtain, while departure airline tickets from China are generally asked for. In addition, if applicants are to visit family members or friends in China, they could be asked to provide the proof of kinship or a letter of invitation from their friends in China.
3. Study Visa (X visa):
X Visa is issued to foreigners who come to China for study for a period of more than six months; it does not allow foreigners to work in China.
The first step is completing the visa application. Be sure to be precise and accurate in your student information. In addition to this every applicant wishing to enter China must have an authorized JW201 or JW202 form. This is a Foreign Student Application Form that is issued by the Chinese State Education Ministry. In addition to these two forms, applicants must also have a letter or enrollment from the University they are going to attend.
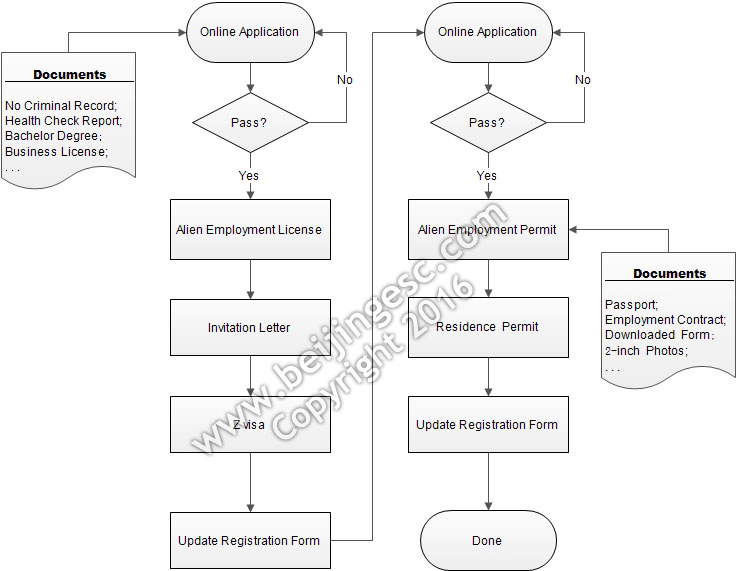
4. Employment/Work Visa (Z visa):
For this visa option applicants must provide the Work Permit and Visa Notification Form for Z Visa, when submitting the Z visa application. Applicants’ Chinese employer should get these two documents in China and then deliver them to the applicants to assist their visa application.
This visa is a little complicated as although the applicants obtain Z visa they are still not permitted to live in China for long. Generally the Z visa approved to applicants just has the validity of 30 days. In the 30 days after entering China, applicants must get a health certificate through a local appointed hospital. During the same time, they also have to be issued the Work Certificate and Residence Permit, for both of which the Chinese employer will complete all the necessary paperwork and arrangements in most cases.
5. Transit Visa (G visa):
A valid visa of the destination country and a succession or round trip airline ticket are required.
6. Journalists Visa (J1 and J2 Visa):
For Journalist’s “J-1”or“J-2”Visa, please first contact the Press Offices of the Chinese Embassy or Consulate-General of PR C in the country where the applicant resides or works permanently.
7. Crew Visa (C visa):
Crew members working on private or charter planes are required to apply visas with business letters from their employing companies. Only after the flying permits are obtained from relevant Chinese authority could the said crew visas come into effect.
8. Resident Visa (D visa):
Applicants for resident visas shall firstly apply for residence permit in person or through their relatives in China with the local Entry and Exit Administration Division under Public Security Department. When the permit is obtained, applicants may apply for a resident visa at this section by submitting the residence permit from the said division.
9. Diplomatic and Service Visa
For the foreign government officials, staff of the United Nations, or other international organizations who are traveling to China for official mission or accreditation, an official note from the governments of their respective countries or from the United Nations, and sometimes a letter or telegram or pertinent document from the competent department of the Chinese Government is required.
Terms Explanation
-
Number of entries refers to the number of times that visa holder is allowed to enter the Mainland China within visa validity. Visa may automatically expire when the given entry times are used out. In case there is still valid entry left while the visa validity is over, reapplication of visa is necessary. Traveling on a visa with no valid entry time results in refusal of entry at the border checkpoint. It is therefore suggested, before departing for the mainland China, to double check the number of entries and the validity of visa.
-
Validity shown as “enter before” in visa refers to the time limit of visa. Visa holder is allowed to enter through the border checkpoint before 24:00 on the exact day of expiration. Visa expires after validity limit and cannot be extended no matter whether there is number of entry left. All visas come into force from the dates of issuance. Traveling on expired visas will result in refusal of entry at the border checkpoint. It is therefore suggested to double check the validity to confirm the visa to be good to use.
-
Duration of stay refers to the maximum days visa holder is allowed to stay in the Mainland China each time, which is counted from the date of entry. If extension of the duration of stay is needed, application should be made at local public security authorities before visa expires. In case of overstaying, punishments such as fines will be made. It is therefore suggested to check visa to avoid overstaying in the Mainland China.